MagThief
Zhenxian Hu 1 , Guangtao Xue 1
National Taiwan University 2
Abstract
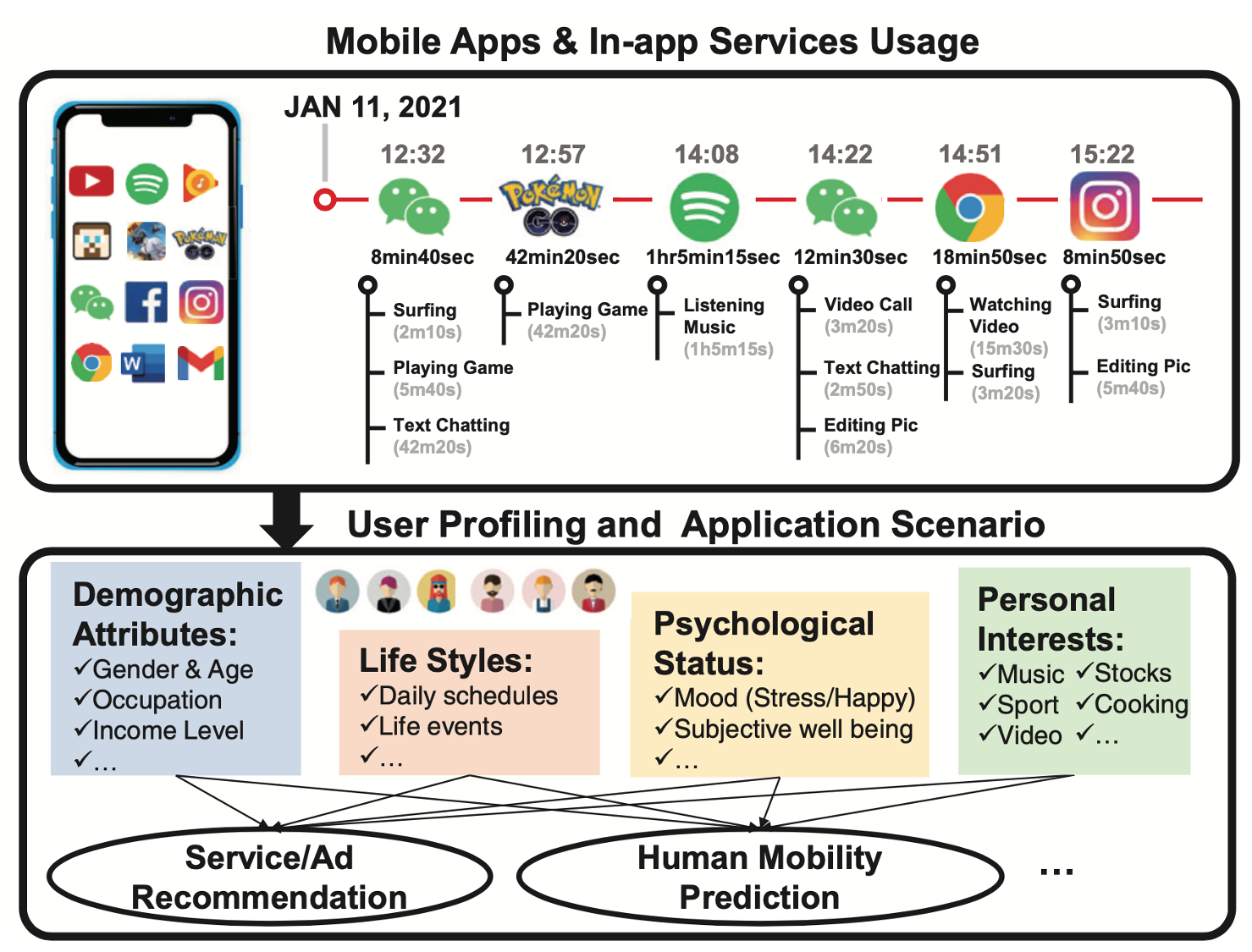
Various characteristics of mobile applications (apps) and associated in-app services have been used reveal potentiallysensitive user information; however, privacy concerns have prompted third-party apps to rigorously restrict access to data related to mobile app usage. This paper outlines a novel approach to the extraction of detailed app usage information based on analysis of the electromagnetic (EM) signals emitted from mobile devices when executing app-related tasks. Note that this type of EM leakage becomes high-complex when multiple apps are used simultaneously and is subject to interference from geomagnetic signals generated by device movement. This paper proposes a deep learning-based multi-label classification system to identify apps and in-app services based on magnetometer readings. The proposed MAGTHIEF system uses accelerometer and gyroscope data to cancel out the offset in geomagnetic signals followed by an elaborate deep region convolution neural network (DRCNN) to differentiate among multiple apps and the corresponding inapp services. Experiments on 50 apps demonstrated the efficacy of MAGTHIEF in identifying multiple apps and in-app services, achieving high average macro F1 scores of 0.87 and 0.95, respectively. MAGTHIEF also achieved time duration accuracy of 89.5% in recognizing app trajectory in the real-world scene